Background: The tumor microenvironment (TME) plays a role in follicular lymphoma (FL) pathogenesis and survival. PD-1/PDL-1 inhibitors have been effective in non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes, such as primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma, and pembrolizumab + rituximab (P-R) produced a complete response (CR) in 50% of patients with rituximab-sensitive, relapsed/refractory (R/R) FL (Nastoupil ASH 2017, Blood Adv 2022). In 2018, we conducted a phase 2 study to assess the efficacy and safety of P-R in R/R FL and diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) including rituximab-resistant patients.
Methods: This phase 2, single-center, open-label, non-randomized trial aimed to determine the objective response rate (ORR) of P-R in R/R FL (Arm A) and R/R DLBCL (Arm B). A 3 rd arm with P + Obinutuzumab (O) for R/R FL was added later (Arm C). Eligible patients had R/R disease; for FL, patients must have received prior anti-CD20 therapy and have an indication for treatment; for DLBCL, patients must have relapsed after or be ineligible for autologous stem cell transplantation. Arm A sought to include > 9 patients with rituximab-refractory disease.
Weekly R 375 mg/m2 x 4 and 4 doses of P (200 mg in q21 day cycles) were given as induction; responders could receive extended P monotherapy for up to 2 years. In Arm C, patients received weekly O x 4; those with at least SD and clinical benefit could receive P for up to 2 years and 6 more doses of O given every 3 months. CT was used for on-treatment tumor assessments after cycles 4 and 8, then every 12 weeks.
A 2-stage design required response at cycle 4 among at least 3 of the first 7 patients in Arm A, and among 3 of the first 9 patients in Arm B, to permit accrual to 20 (Arm A) and 17 patients (Arm B). In Arm C, at least 6 responses in the first 12 patients would be needed to proceed to total accrual of 25 patients. Additional stopping rules were included for excess deaths (>10%) and serious adverse events (SAEs) (>50%).
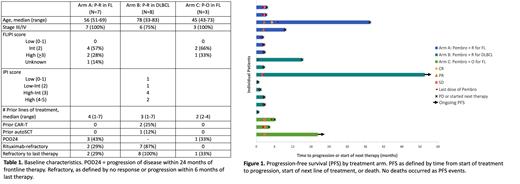
Results: Between 4/2018 and 11/2021, 18 patients were treated on study (Table 1). All were previously treated with rituximab, with 9 refractory to their last rituximab-containing regimen. Median age was 56, 78, and 45 and median prior lines of therapy was 4, 3, and 2 in Arms A, B, and C respectively. In Arm A, 2/7 patients had rituximab-refractory disease, and int- or high-risk FLIPI. All patients in Arm B were refractory to their most recent line of therapy, and 75% had IPI > 3.
In Arm A, ORR was 29% (1 CR, 1 PR). In Arm B, no patients responded (6 PD, 1 SD, 1 unevaluable). In Arm C, 3 were accrued and achieved SD as best response. Figure 1 shows outcomes of all accrued patients.
Treatment-related adverse events (AE) occurred in 83% of patients, with 9 grade 3/4 AEs occurring in 5 (28%) patients (1 acute kidney injury, 2 diarrhea, 1 hypokalemia, 1 arthralgia, 1 infusion reaction, 1 back pain, 1 generalized muscle weakness, 1 heart failure). There were 5 possible grade 3/4 immune-related AEs, including 2 suspected colitis treated with steroids. With a median follow up of 4.2 years, there were 8 deaths, 6 from progressive lymphoma, 1 from AML likely related to prior therapy, and 1 from a combination of progressive lymphoma and therapy-related AML.
Arms A and B closed due to futility, having failed to exceed minimum efficacy for further accrual. Arm C was closed after demonstration of no responses and discussion with the study sponsor following accrual of 3 patients.
Conclusion: P-R has modest, expected toxicity but low efficacy in R/R FL and DLBCL patients previously treated with R. Our data align with CHECKMATE-140 in FL (4% ORR, Armand Blood 2021) and data from post-transplant DLBCL (10% ORR post-ASCT, Ansell JCO 2019). Despite similarities in age and FLIPI distribution with data from Nastoupil et al, we failed to confirm those efficacy findings, a finding partly attributable to inclusion of rituximab-resistant patients. Our data suggest limited utility of combined anti-CD20 and anti-PD-1 therapy in R/R FL and DLBCL, and support exploration of alternative strategies to target the TME in these diseases.
OffLabel Disclosure:
Gopal:Compliment Corporation: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company; Incyte, Kite, Morphosys/Incyte, ADCT, Acrotech, Merck, Karyopharm, Servier, Beigene, Cellectar, Janssen, SeaGen, Epizyme, I-Mab bio, Gilead, Genentech, Lilly, Caribou, Fresenius-Kabi: Consultancy; Merck, I-Mab bio, IgM Bio, Takeda, Gilead, Astra-Zeneca, Agios, Janssen, BMS, SeaGen, Teva, Genmab: Research Funding. Ujjani:Epizyme: Consultancy; Kite, a Gilead Company: Consultancy, Other: Travel expenses , Research Funding; Astrazeneca: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Lilly: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; PCYC: Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Honoraria; Beigene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Atara: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Lynch:Genentech: Research Funding; SeaGen: Research Funding; SeaGen: Consultancy; Cancer Study Group: Consultancy; Rapt: Research Funding; Foresight Diagnostics: Consultancy; Cyteir: Research Funding; Bayer: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; Abbvie: Consultancy; Merck: Research Funding. Poh:Incyte: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy; BeiGene: Consultancy; Acrotech: Consultancy. Fromm:Merck: Research Funding. Smith:ADC Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Epizyme, Karyopharm, KITE pharma, Incyte, Numab Therapeutics AG, Abbvie, Coherus Biosciences, advisory board (spouse) Genentech, Inc.: Consultancy; BeiGene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; ADC Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Ayala (spouse), Bayer, BeiGene, Bristol Myers Squibb (spouse), De Novo Biopharma, Enterome, Genentech, Inc., Ignyta (spouse), Incyte Corporation, Kymera Therapeutics, Merck Sharp and Dohme Corp., MorphoSys, Nanjing Pharmaceu: Research Funding.
Pembrolizumab is a PD-1 inhibitor, which causes the activation of T-cell mediated immune responses against tumor cells.